[ad_1]
The ‘Ledger hacker’ who siphoned away at the least $484,000 from a number of Web3 apps on Dec. 14 did so by tricking Web3 customers into making malicious token approvals, based on the staff behind blockchain safety platform Cyvers.
In line with public statements made by a number of events concerned, the hack occurred on the morning of Dec. 14. The attacker used a phishing exploit to compromise the computer of a former Ledger employee, having access to the worker’s node package deal supervisor javascript (NPMJS) account.
We have now recognized and eliminated a malicious model of the Ledger Join Equipment.
A real model is being pushed to switch the malicious file now. Don’t work together with any dApps for the second. We are going to hold you knowledgeable because the state of affairs evolves.
Your Ledger system and…
— Ledger (@Ledger) December 14, 2023
As soon as they gained entry, they uploaded a malicious replace to Ledger Join’s GitHub repo. Ledger Join is a generally used package deal for Web3 functions.
Some Web3 apps upgraded to the brand new model, inflicting their apps to distribute the malicious code to customers’ browsers. Web3 apps Zapper, SushiSwap, Phantom, Balancer, and Revoke.money had been contaminated with the code.
Consequently, the attacker was capable of siphon away at the least $484,000 from customers of those apps. Different apps could also be affected as nicely, and experts have warned that the vulnerability might have an effect on the complete Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM) ecosystem.
The way it may have occurred
Talking to Cointelegraph, Cyvers CEO Deddy Lavid, chief expertise officer Meir Dolev, and blockchain analyst Hakal Unal shed additional mild on how the assault might have occurred.
In line with them, the attacker seemingly used malicious code to show complicated transaction information within the consumer’s pockets, main the consumer to approve transactions they didn’t intend to.
When builders create Web3 apps, they use open-source “join kits” to permit their apps to attach with customers’ wallets, Dolev acknowledged. These kits are inventory items of code that may be put in in a number of apps, permitting them to deal with the connection course of without having to spend time writing code. Ledger’s join package is likely one of the choices out there to deal with this process.
It seems like at this time’s safety incident was the fruits of three separate failures at Ledger:
1. Blindly loading code with out pinning a selected model and checksum.
2. Not implementing “2 man guidelines” round code evaluation and deployment.
3. Not revoking former worker entry.— Jameson Lopp (@lopp) December 14, 2023
When a developer first writes their app, they normally set up a join package by means of Node Bundle Supervisor (NPM). After making a construct and importing it to their website, their app will comprise the join package as a part of its code, which can then be downloaded into the consumer’s browser at any time when the consumer visits the positioning.
In line with the Cyvers’ staff, the malicious code inserted into the Ledger Join Equipment seemingly allowed the attacker to change the transactions being pushed to the consumer’s pockets. For instance, as a part of the method of utilizing an app, a consumer usually must situation approvals to token contracts, permitting the app to spend tokens out of the consumer’s pockets.
The malicious code might have prompted the consumer’s pockets to show a token approval affirmation request however with the attacker’s tackle listed as an alternative of the app’s tackle. Or, it might have prompted a pockets affirmation to seem that will encompass difficult-to-interpret code, inflicting the consumer to confusedly push “affirm” with out understanding what they had been agreeing to.
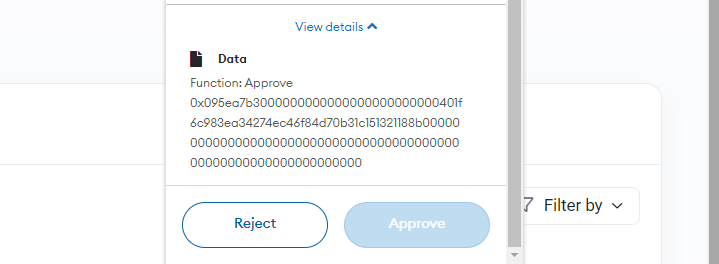
Blockchain information exhibits that the victims of the assault made very giant token approvals to the malicious contract. For instance, the attacker drained over $10,000 from the Ethereum tackle 0xAE49C1ad3cf1654C1B22a6Ee38dD5Bc4ae08fEF7 in a single transaction. The log of this transaction exhibits that the consumer approved a really great amount of USDC to be spent by the malicious contract.

This approval was seemingly carried out by the consumer in error due to the malicious code, mentioned the Cyvers staff. They warned that avoiding this sort of assault is extraordinarily troublesome, as wallets don’t at all times give customers clear details about what they’re agreeing to. One safety follow which will assistance is to fastidiously consider every transaction affirmation message that pops up whereas utilizing an app. Nonetheless, this may increasingly not assist if the transaction is displayed in code that’s not simply readable or is complicated.
Associated: ConsenSys exec on MetaMask Snaps security: ‘Consent is king’
Cyvers claimed that their platform permits companies to verify contract addresses and decide if these addresses have been concerned in safety incidents. For instance, the account that created the sensible contracts used on this assault was detected by Cyvers as having been concerned in 180 safety incidents.

Whereas Web3 instruments sooner or later may enable assaults like these to be detected and thwarted prematurely, the business nonetheless has “a protracted technique to go” in fixing this downside, the staff advised Cointelegraph.
[ad_2]
Source link





